The electrocardiogram is a medical study that reflects the mechanisms and impulses of the heart, such as arrhythmias, blood insufficiency (infarcts), which are taken through electrodes connected to the patient’s body, and the same, are studied, through the electrocardiograph, and the signals that it emits.
This study is achieved the recording and visualization from a screen, which captures signals and leads in the form of waves, which translate into patterns of electrical impulses that transfer from the patient’s heart. The appearance of the pattern contributes to the diagnosis of some anomaly present. The interpretation of the electrocardiogram, essential for the knowledge and development of every doctor to know how to interpret the cardiovascular manifestations of patients.
Types of Referrals
The correct interpretation of the electrocardiogram has to be developed by a group of specialists for the care of patients who require it, either in emergency services, personal consultations, operating theaters, etc. It is necessary to understand the management of the electrocardiogram leads, for the interpretation of the heart manifestations, and understand electrical, mechanical and acoustic events, which are the cornerstone of the function and indispensable for the clinician.
For the understanding of the derivations, there are twelve that consist of six standard derivations (I, II, III, aVR, aVL and aVF) and six precordial derivations (V1, V2, V3, V4, V5 and V6). The standard derivations are called bipolar (I, II and III) and augmented (aVR, aVL and aVF), which are explained as follows:
- Bypass I: It tracks the voltage contrast between the left arm and right arm electrodes.
- Bypass II: The voltage difference between the electrodes of the left leg and the right arm.
- Bypass III: The voltage discrepancy between the left leg and left arm electrodes.
The elevated leads analyze the frontal plane of electrical activity by recording the voltage of the corresponding limb:
- aVR placed on right arm
- aVL placed on left arm
- aVF placed on left foot
The precordial leads are installed in such a way that the reading of the electrical activity can divide the heart in a horizontal plane. They are in charge of reporting the action of the vector in the anterior or posterior direction, right or left, but they cannot see superior or inferior but when combining the two planes (frontal and precordial) we obtain the three-dimensional behavior of the vector being able to observe it up or down, right or left, anterior or posterior.
Thus, the electrical record of the leads is accompanied by the structures of the heart, so that the variations in any of them do not give an idea of the location of the causal defect, since:
- V1-V2 Septal wall
- V3-V4 Previous Wall
- I, aVL ,V5-V6 Side wall
- II, III, aVF Bottom wall
The collection of these signals is called electrocardiogram (ECG) and is a clear indicator of the behavior and state of the heart.
Interpretation of Electrocardiogram Derivations
Electrodes connected to the electrocardiograph transform the electrical signals in the heart into waves, which are printed on paper, usually immediately, so that the doctor can make the diagnosis.
The result of the electrocardiogram is printed on a grid paper, in which each frame is 1 mm, corresponding to 0.04 seconds and a set of 5 squares forms a large square of 5 mm or 0.20 seconds, therefore 5 large squares equals 1 second. On the vertical axis, the voltage is represented and on the horizontal the time. 10 mm high equals 1 voltage of 1mV.
The normal rhythm of an ECG is formed by a P wave, a QRS complex and a T wave. To interpret an electrocardiogram one must assess the presence of these waves, their shape and duration, as well as the ST segment (time between the end of depolarization and the beginning of the ventricular repolarization, it measures less than 1 mm, if greater than 1 mm indicates infarction or ischemia).
The P waves, which allow to know the time between the heartbeats, are represented as a straight line between the lowest and highest point. The T wave represents the small perceptible beat after the first and marks the end of the heartbeat.
The time elapsed between the two must be quite normal throughout the examination, if on the contrary, changes are observed, it is a sign of an irregularity in the heartbeat.
Therefore, it resulted in reading the results of patients who require the relevant tests to know and shed the electrical activities of the heart.
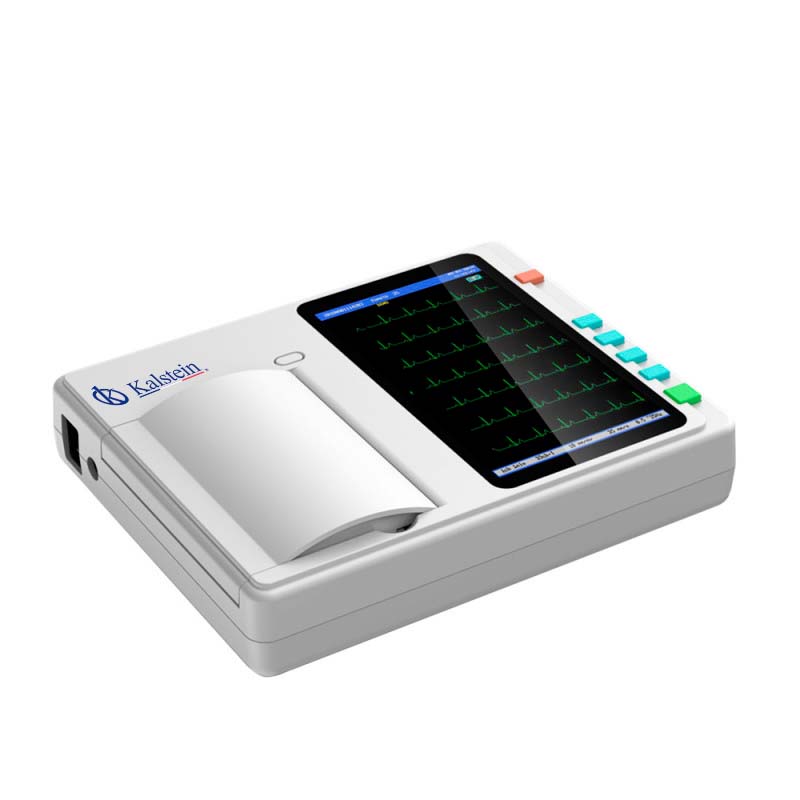
Electrocardiographs brand KALSTEIN
At Kalstein, we are trained to offer you the best medical equipment, capable of meeting the demands that any medical unit requires. Therefore, we offer the 3 channel ECG machine prints 3 waveforms / channels at once. In 3-channel machines, the ECG signals selected by the microprocessor are amplified, filtered and sent to a 3-channel multiplexer, YR models, power supply, lifetime warranty, metal and plastic material, class A instrument rating, 7″ color touch screen monitor with super-thin designs, USB ports, storage of up to 30000 patient records and for your best convenience, click on our link HERE